Permittivity Of Free Space Si Units

Permittivity as a function of frequency can take on real or complex values.
Permittivity of free space si units. From the centimetre gram second cgs system the value of the permittivity of free space ε 0 is chosen arbitrarily to be 1. Following is the table for its mathematical form and si unit. In si units permittivity is measured in farads per meter f m or a 2 s 4 kg 1 m 3.
In the centimetre gram second or permittivity of free space in cgs system the unit of the permittivity of free space ε 0 is selected arbitrarily to be 1. The permittivity is because of polarization whereas the permeability is because of magnetization. Its units and those of permittivity ε are square coulombs per newton square metre.
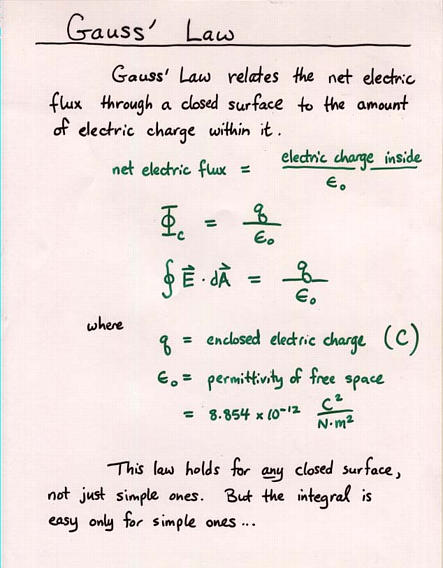
The free space of the permittivity is 8 85 f m whereas that of the permeability it is 1 26 h m. The physical constant ε0 pronounced as epsilon nought or epsilon zero commonly called the vacuum permittivity permittivity of free space or electric constant or the distributed capacitance of the vacuum is an ideal baseline physical constant which is the value of the absolute dielectric permittivity of classical vacuum. In the rationalized metre kilogram second mks and si systems the magnitude of the permittivity of a vacuum ε 0 is 8 854 10 12.
The vacuum characterizes the least possible value of permittivity. Other materials specifically dielectrics have a permittivity that is related to their electric susceptibility χ e which is a measure of how polarizable a material is in the presence of an electric field. This is commonly referred to as the permittivity of free space or electric constant.
Denoted by ϵ 0 and has the value 8 85 10 12 faraday meter. The absolute permittivity is a proportionality constant between the electric and. The absolute permittivity of a medium is its relative permittivity multiplied by the vacuum permittivity.
The displacement field d is measured in units of coulombs per square meter c m 2 while the electric field e is measured in volts per meter v m.