Spacing Effect Psychology Definition
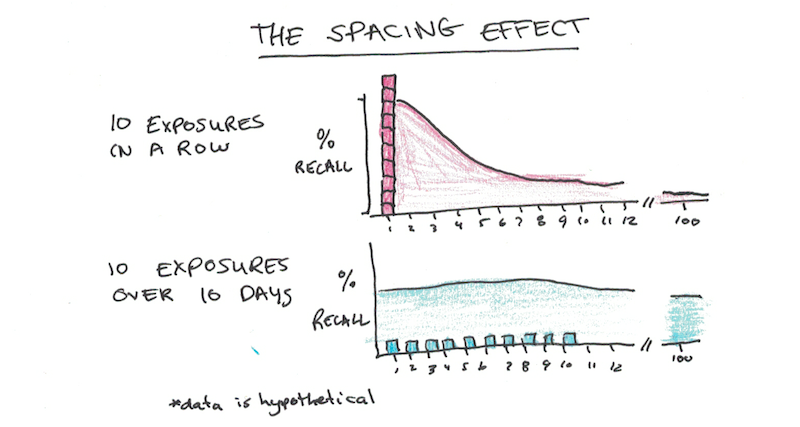
The spacing effect demonstrates that learning is more effective when study sessions are spaced out.
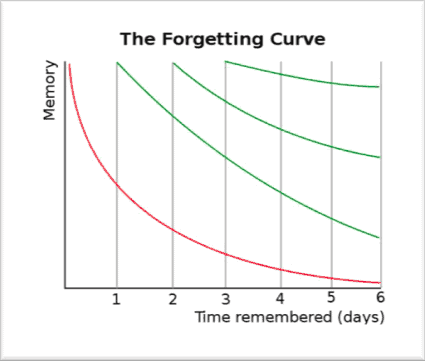
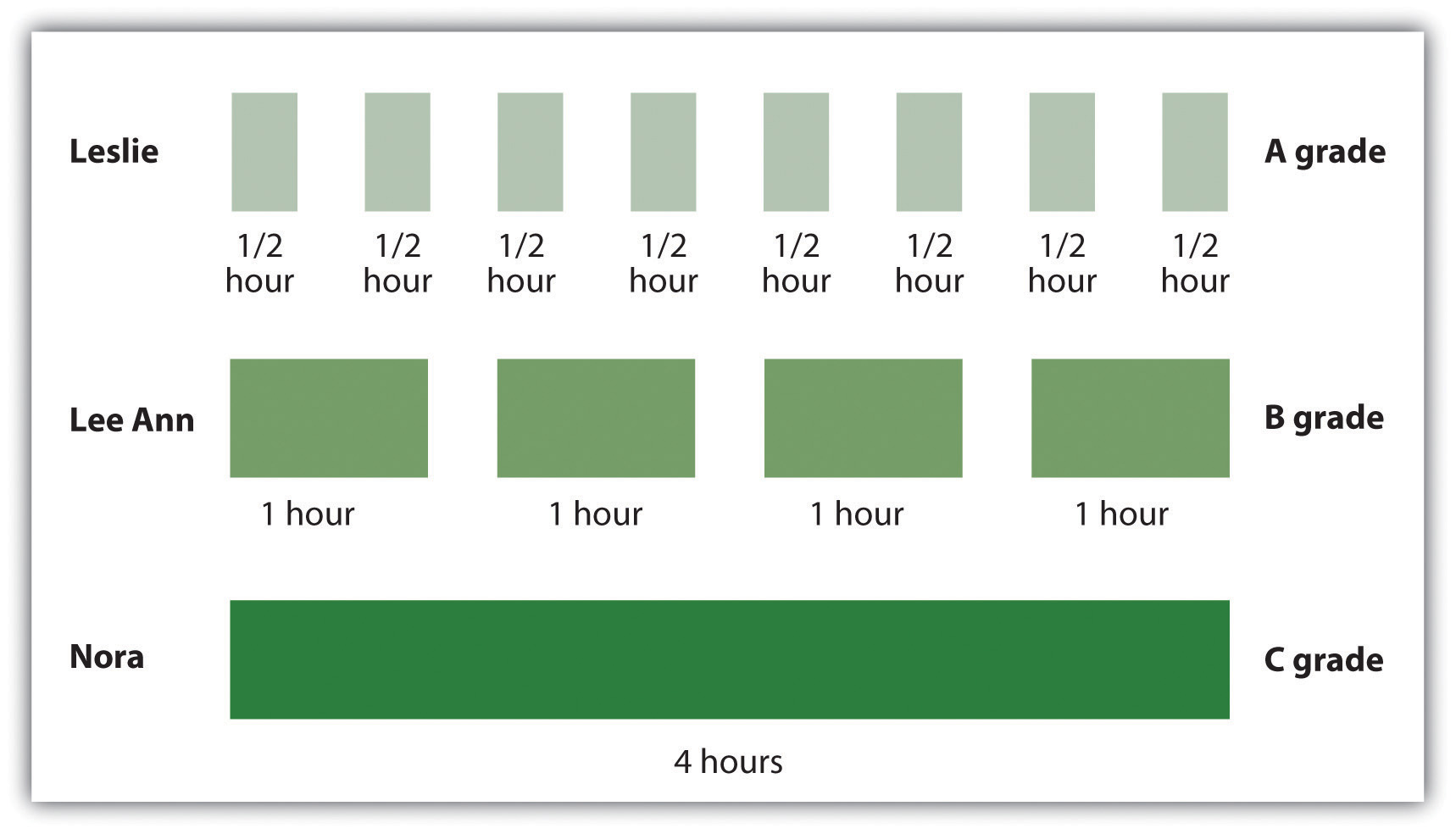
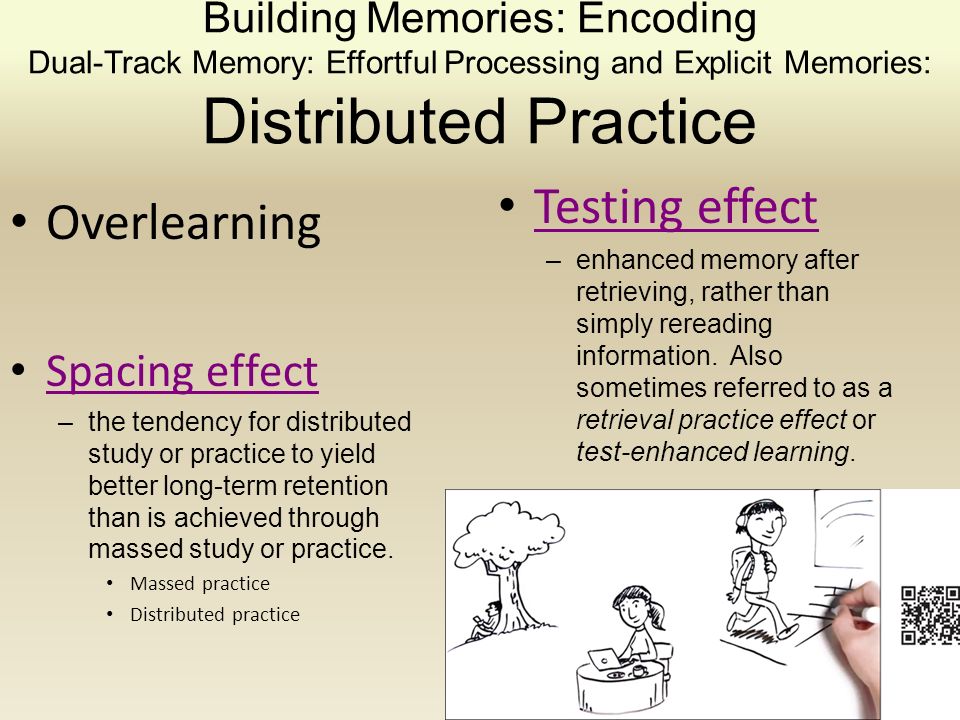
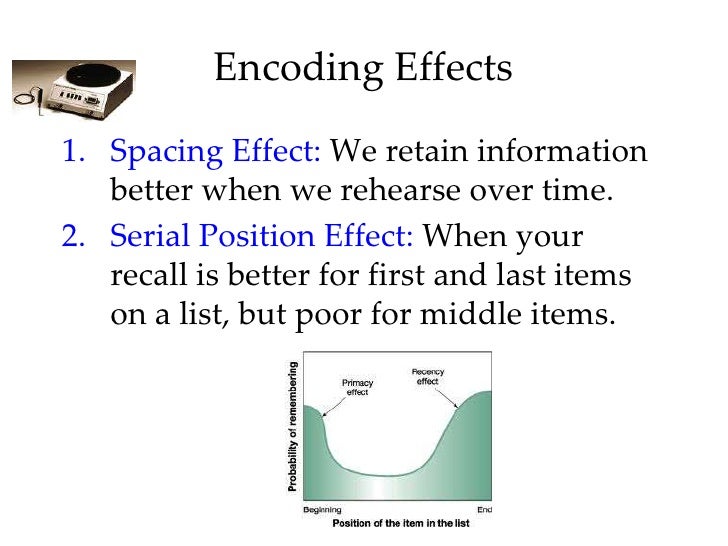
Spacing effect psychology definition. Study phase retrieval accounts propose that spacing effects occur when upon the second presentation of an item people retrieve the prior presentation and additional information is added to the memory trace when the prior presentation is retrieved greene 1989. The spacing effect is the tendency for long term memory to be increased when learning events are spaced in time. 3 generally speaking multiple practice sessions over time results in better long term memory than a single practice session of equivalent duration or an equivalent number of repetitions.
This effect has been demonstrated in over 200 research studies from over a century of research. The spacing effect in the field of psychology the spacing effect refers to the finding that information which is presented over spaced intervals is learned and retained more easily and more effectively. The benefit of distributing learning over time is commonly known as the spacing effect.
The spacing effect refers in psychology to the observed phenomenon that items that are repeated during list learning are remembered better if their two presentations are spread out over time spaced presentation than immediately one after the other massed presentation. Hintzman block 1973. Spacing effect states that we learn material more effectively and easily when we study it several times spaced out over a longer time span rather than trying to learn it in a short period of time.
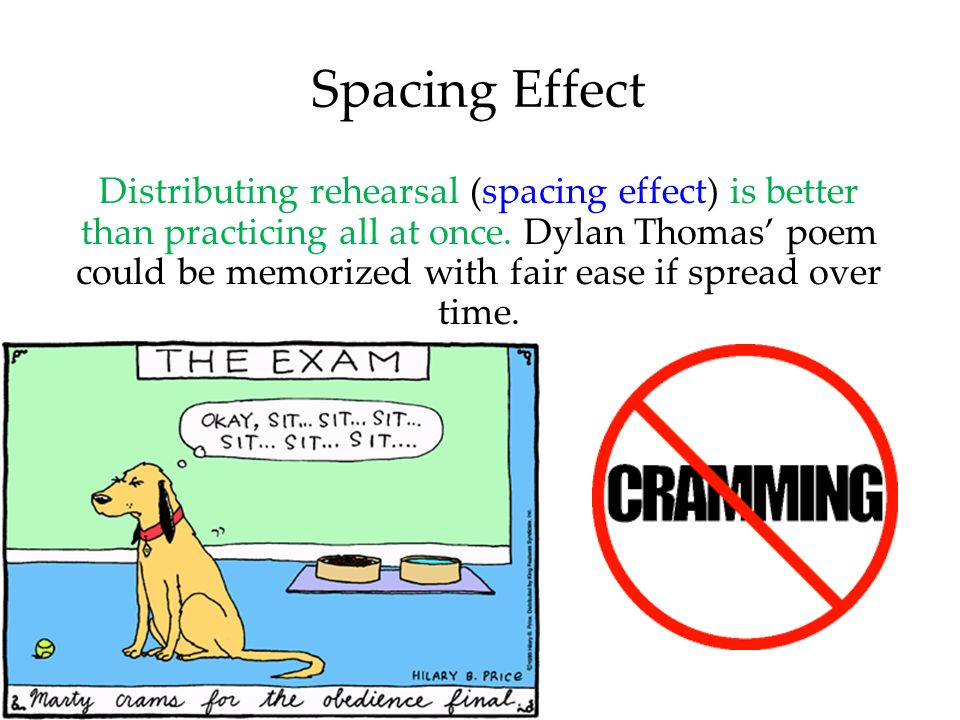
As you can guess this means that cramming for an exam the night before is not as effective as studying material each night over a week or some period of time. In particular it refers to remembering items in a list. It is believed that.
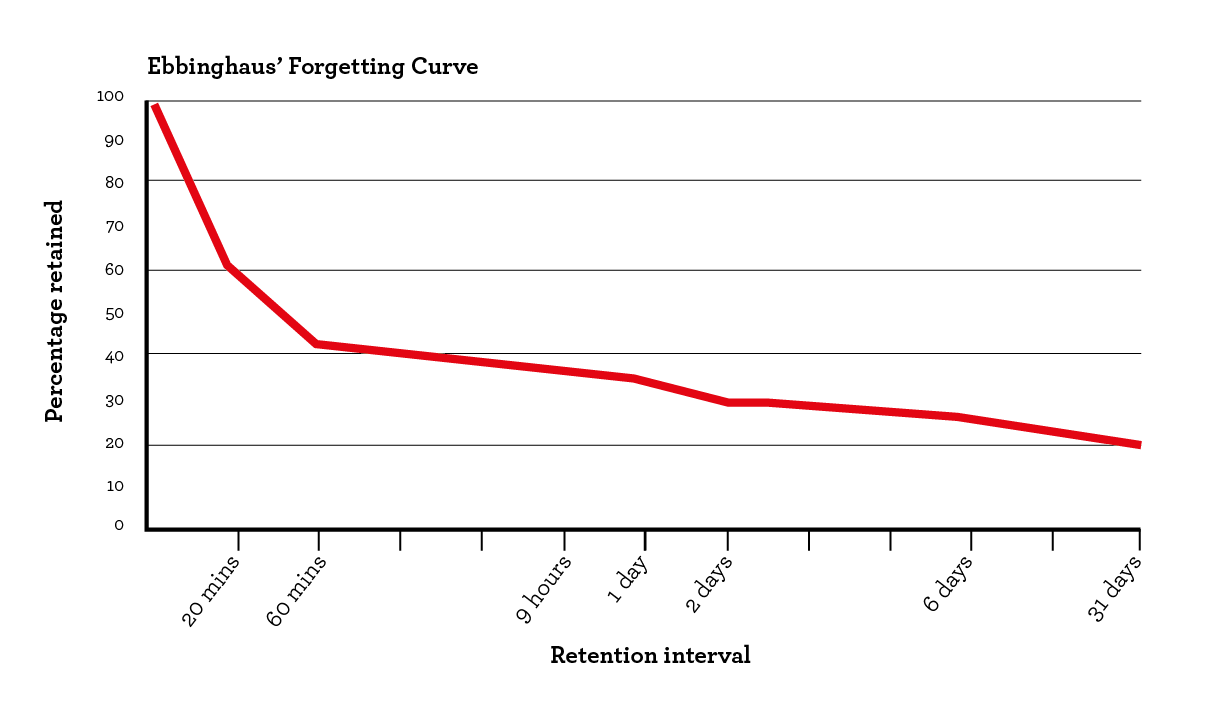
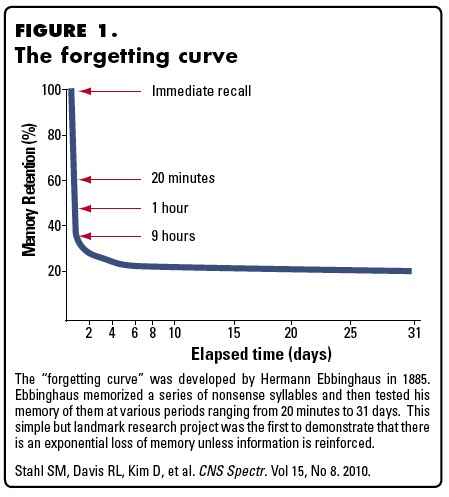
Untersuchungen zur experimentellen psychologie which suggests that. This has broad implications for education communication and marketing. The phenomenon was first identified by hermann ebbinghaus and his detailed study of it was published in the 1885 book über das gedächtnis.